
What's a custom wheel without even more options?
Fuel Off-Road Forged wheels deliver you limitless color and finish options, choices of numerous lip detail designs and
a range of center caps including our customizable billet cap for multiple lug patterns.
Choices.
finishes.
Here's a sampling of our more popular finishes. Of course, the possibilities are endless.

/ gloss black

/ matte silver

/ matte anthracite

/ brushed matte gold

/ gloss bronze

/ brushed gloss candy black

/ gloss brushed

/ gloss brushed single dark tint

/ matte brushed ddt

/ brushed gloss rose gold

/ gloss brushed monaco copper

/ brushed candy copper
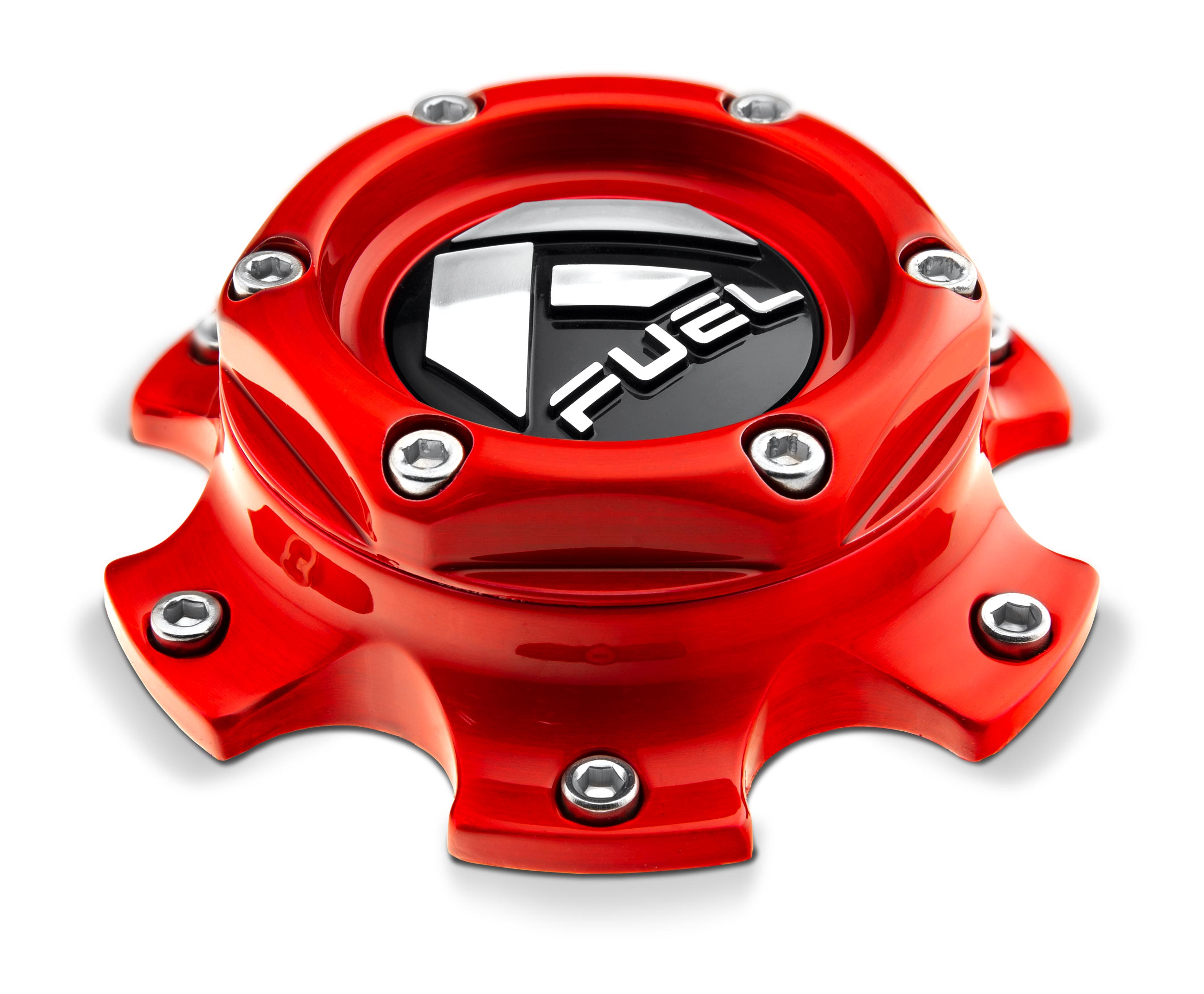

/ brushed candy red
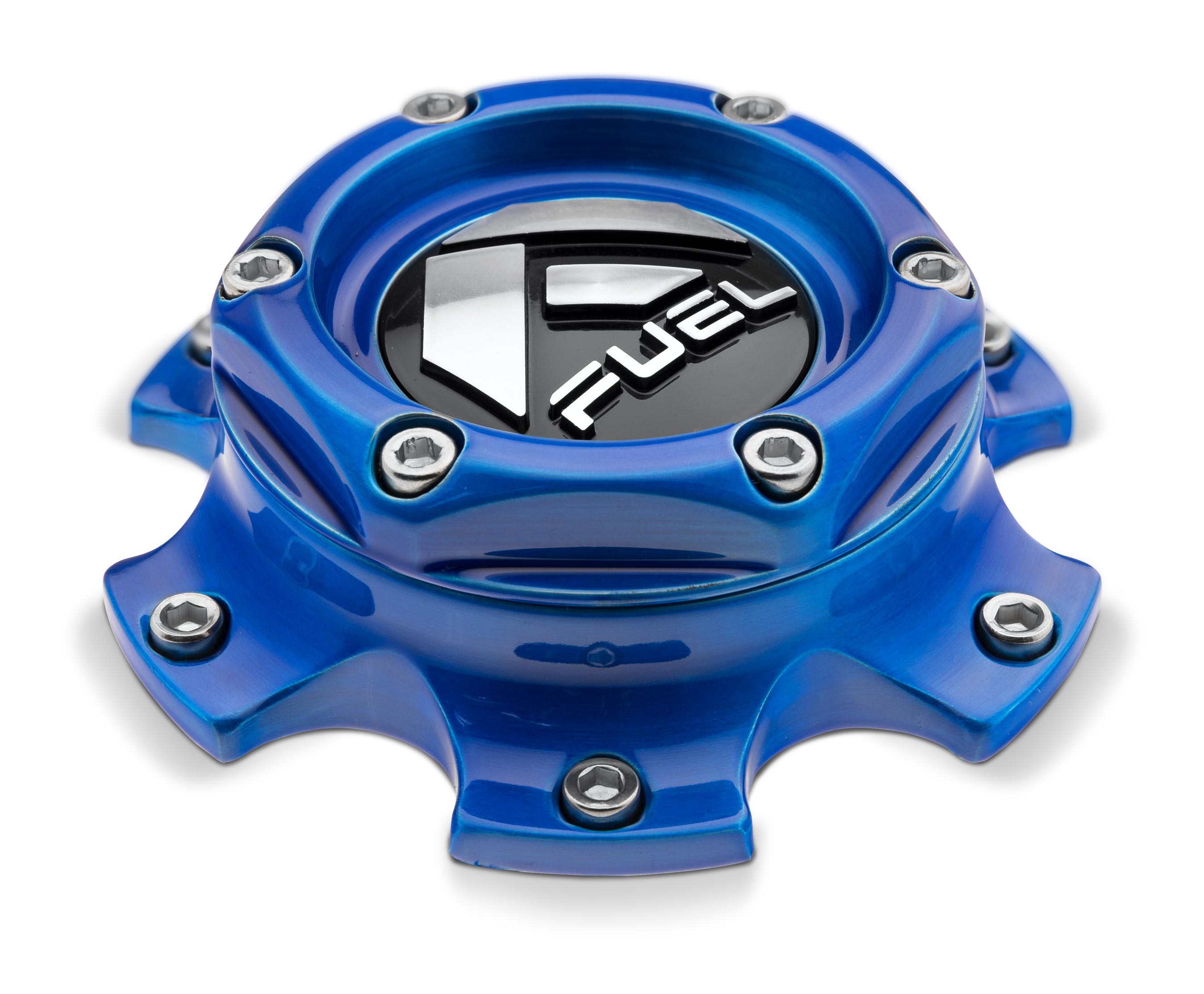

/ brushed gloss candy blue
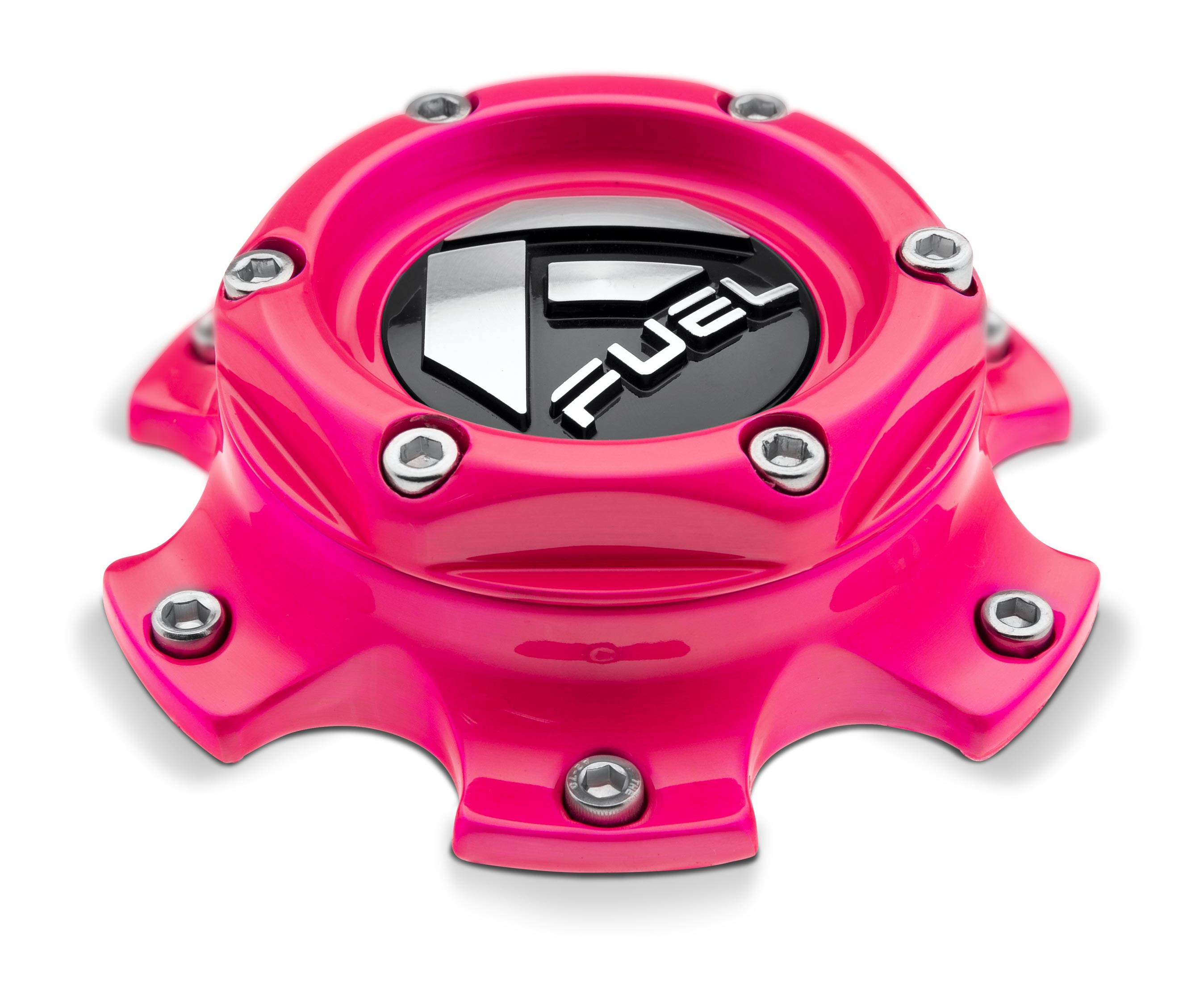

/ gloss candy pink

lip details.
Choose any of these lip detail options when building your forged wheels.
option a
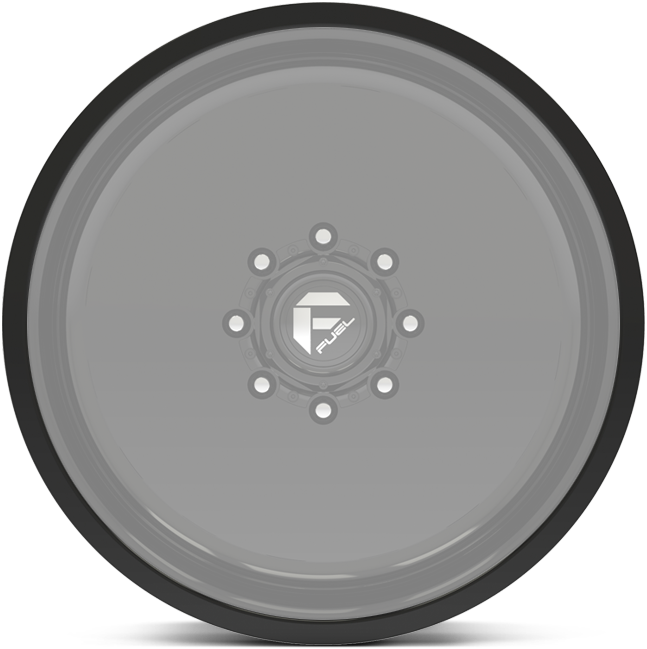

option d
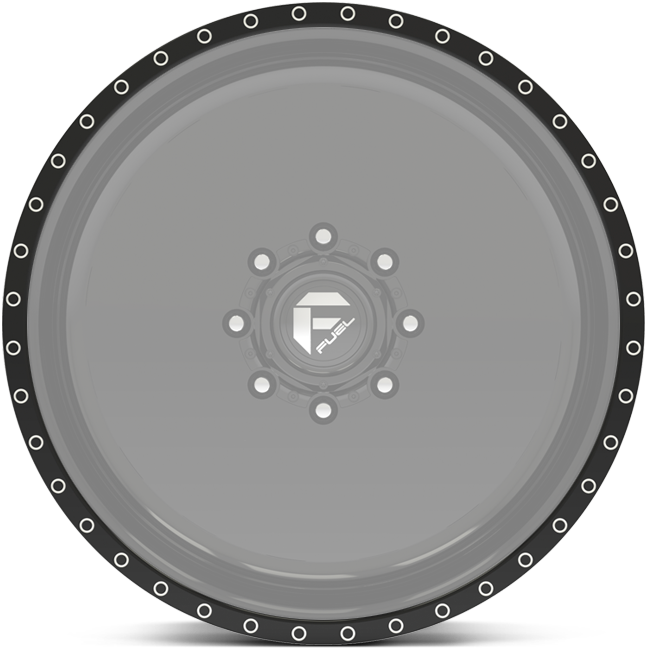
option g

option h
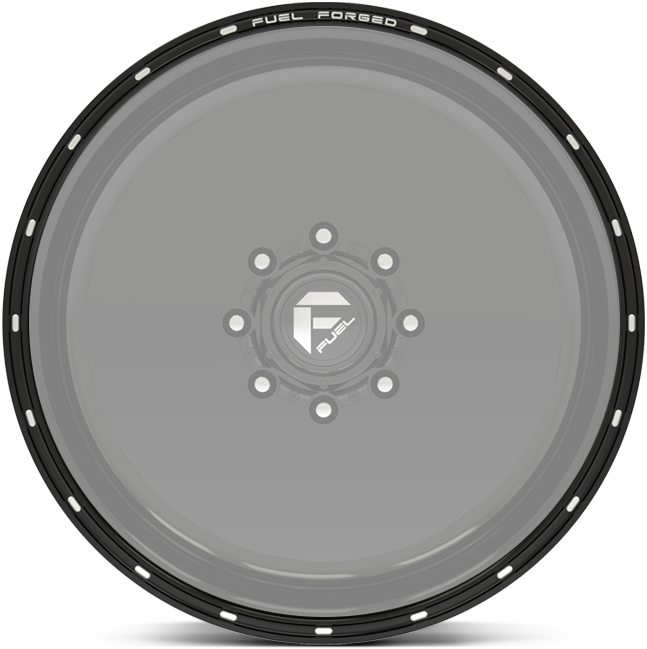
option i
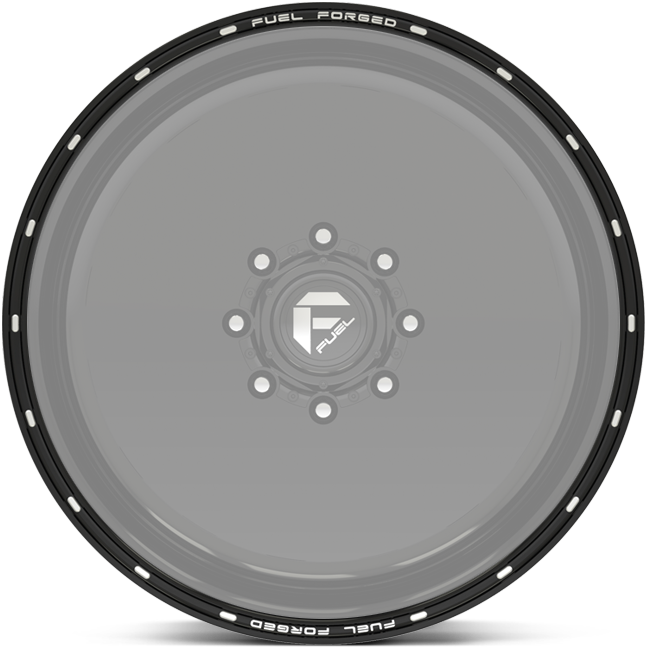
option j
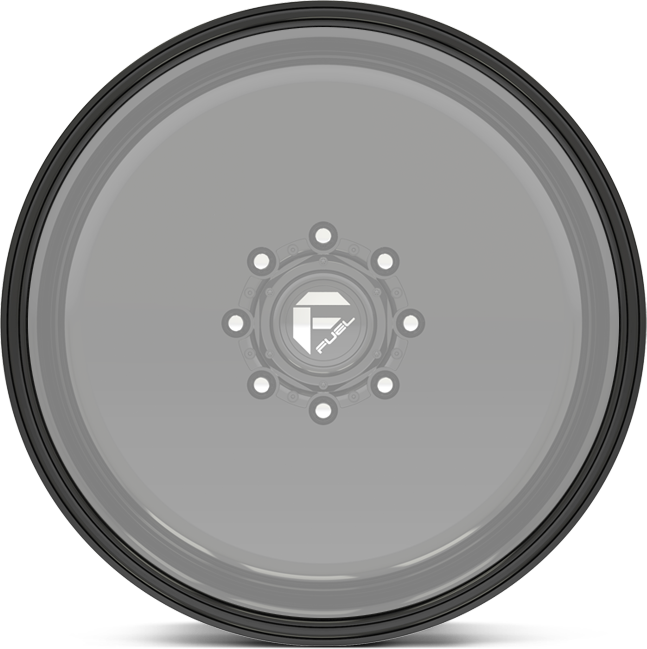
option bb
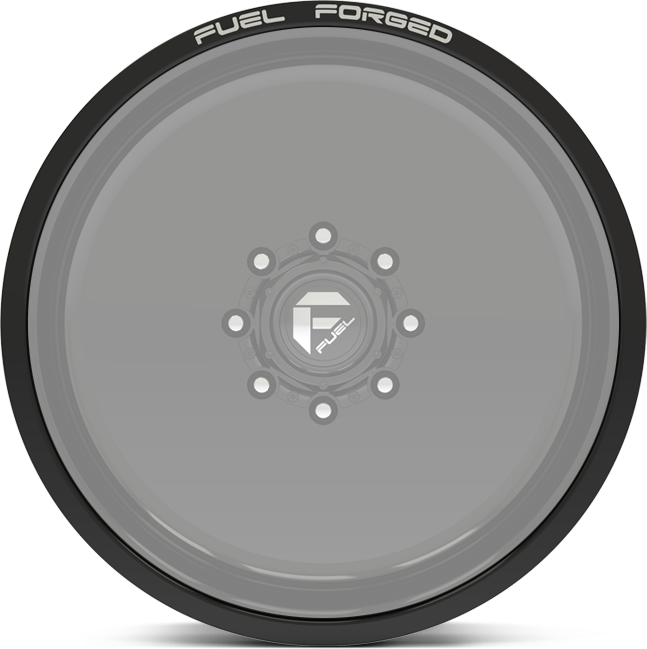
option cc

option ee
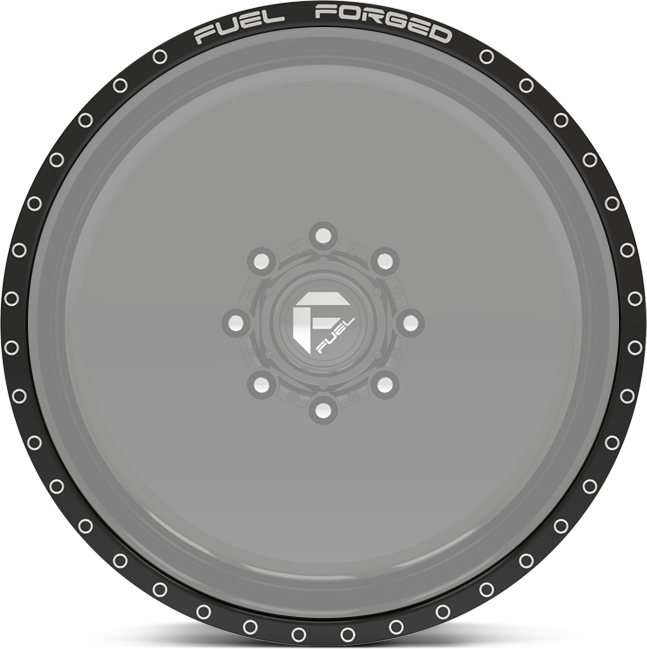
option ff

centercap options.
Three different base cap options (some caps not available for certain wheel designs. ) Availabe in bolt-on forged aluminum, bolt-on plastic and snap-in plastic options. Custom finishes available.


